Blog/2025.12.18
LED display systems are widely deployed in advertising, stage applications, public information platforms, and traffic guidance. During operation, failures such as data corruption, signal interruption, or hardware malfunction may result in display outages, degraded performance, or safety risks. To maintain system availability and operational continuity, LED display systems are typically designed with hardware redundancy and data backup architectures, enabling fault tolerance, rapid recovery, and reduced downtime.

1. Definition
LED display system backup refers to safeguard solutions that provide operational security through technologies such as hardware redundancy and data redundancy. When the primary system or critical components malfunction, the backup system can promptly take over or restore operation, ensuring uninterrupted display or rapid recovery.
2. Common Backup Applications
|
Type |
Application |
Functional Description |
|
Hardware / Signal Backup |
Signal Loop |
By configuring the LED display control system in a ring topology, bidirectional or multi-path signal transmission is achieved. In the event of a single-point link failure, the signal can automatically reroute, ensuring continuous display operation. |
|
Power Redundancy |
Dual power supplies or an N+1 power module design are employed. If one power module fails, the remaining modules continue supplying power, preventing partial or total black screens caused by power abnormalities. |
|
|
Dual Sending Cards |
The primary and backup sending cards operate in real-time synchronization. When the primary sending card fails, the backup card can automatically or rapidly take over output, enabling seamless switching with no black screen or frame drop. |
|
|
Data Backup |
Playback Content |
Display content is backed up locally or remotely to prevent the loss of critical materials due to storage media failure, accidental deletion, or other unexpected incidents. |
|
Configuration Parameters |
Control system parameters—such as resolution settings, brightness levels, and calibration data—are backed up to allow fast restoration during equipment replacement or system recovery. |
|
|
System Software |
Control software or control card firmware versions are backed up, enabling version rollback and rapid recovery after system failures. |
3. Importance of Backup
· Ensuring Continuous Operation
Any interruption in the display can negatively impact user experience and reduce commercial value. Backup hardware helps prevent system downtime caused by single-point failures, while data backup protects display content and configuration parameters from loss, ensuring uninterrupted system operation.
·Reducing Failure Risks
Hardware aging, software anomalies, and power supply issues can all lead to display outages. Through well-designed backup and redundancy architectures, systems can achieve rapid switchover or recovery in the event of failures, significantly reducing maintenance time and operational risks.
· Enhancing Safety and Stability
In critical application scenarios such as traffic signage, stadiums, and large public squares, display malfunctions may create safety hazards or result in substantial economic losses. Comprehensive backup and redundancy mechanisms are fundamental to ensuring safe, stable, and reliable system operation.
4. Product Application Example
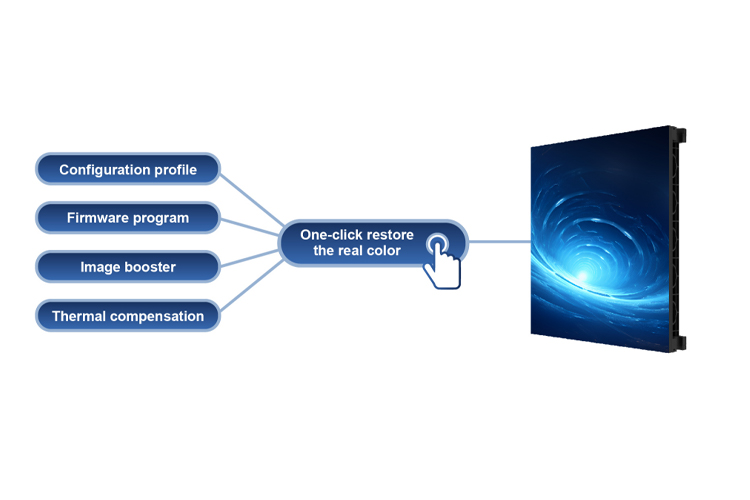
The YES TECH MG10 supports dual backup of calibration coefficients, providing an additional layer of protection for screen commissioning and daily operation. This feature ensures higher system stability and reliability. In practical applications, the YES TECH MG10 enables users to restore optimal display performance through one-click switching, greatly reducing adjustment time and workload—delivering a truly efficient, time-saving, and worry-free user experience.
+86-(0)731-84539619
Hunan Yestech Optoelectronic Co., Ltd. Terms of Service Privacy Policy Powered by szweb